Lipolysis Kits

Lipolysis plays a central role in the regulation of energy balance. Lipolysis is the process in which triglycerides (TG) are hydrolyzed into glycerol and free fatty acids. This process releases free fatty acids (FFA) into the bloodstream where they may be either re-esterified by the adipocyte or travel to other tissues and exert other effects throughout the body. Elevated adipocyte lipolysis has been observed in obese and diabetic individuals (Arner 1996). Excessive free fatty acid production is believed to contribute to insulin resistance in skeletal muscle that is observed in obesity. Hormone sensitive lipase is the rate-limiting enzyme catalyzing triglyceride breakdown. Perilipins, one of the PAT (perilipins, adipophilin, TIP47 proteins) family of lipid-associated proteins, are implicated in adipocyte lipolysis by mediating the interaction of HSL with the triacylglycerol molecule (Brasaemle et al. 2004; reviewed in, Tansey et al. 2004.) The presence of these proteins corresponds to lipolytic stimulation in cultured adipocytes (Braemle et al. 2004).
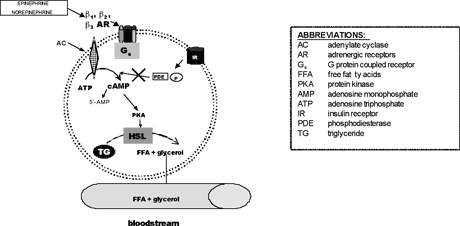
The sympathetic nervous system also plays a key role in the regulation of lipid mobilization. The main lipolytic pathway involves beta-agonists (β-agonists), which activate β-adrenergic receptors via the intracellular Gs proteins in adipocytes. This leads to the activation of adenylate cyclase (AC), which then increases cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels. Elevated cAMP acts as a second messenger to activate hormone sensitive lipase (HSL). HSL, the rate-limiting enzyme regulating adipocyte lipolysis, then catalyzes the hydrolysis of triglycerides and results in the release of glycerol and FFA (increased lipolysis). Phosphodiesterases (PDE) are enzymes that hydrolyze cAMP to 5'-AMP (5 prime adenosine monophosphate). This action results in a decrease in lipolysis. PDE inhibitors increase intracellular cAMP levels. 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX), a non-specific inhibitor of cAMP phosphodiesterases (PDE), is used as the positive control if your test compounds are suspected PDE inhibitors. Isoproterenol, a non-specific β-adrenergic agonist is used as the positive control if your test compounds affect lipolysis via β-adrenergic receptors (Robidoux et al. 2004).
Our lipolysis assay kits provide the tool to study chemical compounds that may influence lipolysis in cultured human or 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Kits are available with and without a plate of cells. Kits can measure the glycerol and/or free fatty acids released in lipolysis.
Overview of adipocyte lipolysis
Ordering Information:
Human Lipolysis Assay Kits
| Item# | Item Desc | U/M | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIP-1 | Lipolysis Assay KIT, Glycerol Detection ( REAGENTS+ CELLS) | KIT | $1003.00 |
| LIP-1-NC | Lipolysis Assay KIT , Glycerol Detection (REAGENTS ONLY) | KIT | $487.00 |
| LIP-1-RB | Lipolysis Assay KIT (5 plates; REAGENTS+ BUFFERS ONLY) | KIT | $2006.00 |
| LIP-1-SPF | Lipolysis Assay Kit, Glycerol Detection, WITH Cryopreserved Subcutaneous Preadipocytes (2 million cells) | KIT | $845.00 |
| LIP-2 | Lipolysis Assay KIT, Free fatty acids Detection (REAGENTS+ CELLS) | KIT | $1,157.00 |
| LIP-2-NC | Lipolysis Assay KIT, Free fatty acids Detection (REAGENTS ONLY) | KIT | $662.00 |
| LIP-2-RB | Lipolysis Assay KIT, Free Fatty Acids Detection (5 plates; REAGENTS+ BUFFERS ONLY) | KIT | $2,575.00 |
| LIP-3 | Lipolysis Assay KIT Dual glycerol and free fatty acids Detection (REAGENTS+ CELLS) | KIT | $1,381.00 |
| LIP-3-NC | Lipolysis Assay KIT , Dual Glycerol and free fatty acids Detection (REAGENTS ONLY) | KIT | $863.00 |
| LIP-3-RB | Lipolysis Assay KIT, Dual Glycerol and free fatty acids Detection (REAGENTS ONLY for 5-96 well plates) | KIT | $3,662.00 |
| LIP-6-NC | Lipolysis Assay Kit, Adipose Tissue Explant: Glycerol Detection (REAGENTS ONLY) | KIT | $478.00 |
| LIP-GLYSTAN | Glycerol Standard, for Lipolysis Assay Kits | EACH | $48.00 |
| RGTA-10 | 11-ML Glycerol Reagent A | EACH | $128.00 |
| RGTA-40 | 40-ML Glycerol Reagent A | EACH | $206.00 |
3T3-L1
| Item# | Item Desc | U/M | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| LIP-1-L1 | 3T3-L1 Lipolysis Assay Kit (glycerol detection; REAGENTS+ CELLS) | Kit | $935.00 |
| LIP-1-NC-L1 | 3T3-L1 Lipolysis Assay Kit (glycerol detection; REAGENTS ONLY) | Kit | $487.00 |
| LIP-2-L1 | 3T3-L1 Lipolysis Assay Kit (free fatty acid detection; REAGENTS+ CELLS) | Kit | $1068.00 |
| LIP-2-NC-L1 | 3T3-L1 Lipolysis Assay Kit (free fatty acids detection; REAGENTS ONLY) | Kit | $591.00 |
| LIP-3-L1 | 3T3-L1 Lipolysis Assay Kit (dual glycerol and free fatty acids detection; REAGENTS+ CELLS) | Kit | $1,222.00 |
| LIP-3-NCL1 | 3T3-L1 Lipolysis Assay Kit (dual glycerol and free fatty acids detection; REAGENTS ONLY) | Kit | $863.00 |
* This kit includes one 96-well plate of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, media to differentiate the cells and reagents for the detection of lipolysis.
ZenBio Kits - Recent Publications
LIP-1
- LIP-1-NC lipolysis kit used to quantify glycerol release in hormone stimulated adipocytes (Gagnon, et al., 2010).
- Lipolysis Assay kit used in 3T3L-1 cells and primary adipocytes (Liu, et al., 2009).
- Lipolysis Assay Kit Buffer used to measure adipogenesis regulation by G protein coupled receptor 103 (Mulumba, et al.).
- Lipolysis Assay kit used to measure lipolysis in 3T3 Cells after caveloin-1 knockdown by siRNA (Ahmad, et al., 2009).
- Glycerol Reagent (Lipolysis kit) used to measure lipolysis in 3t3-1 adipocytes following Xanthohumol and guggulsterone treatment (Rayalam, et al., 2009).
- Lipolysis Kit used to measure the glycerol content in the culture medium after isoproterenol treatment (Klein, Schreml, Nerlich, & Prantl, 2009).
- Lipolysis Kit used to measure lipolysis in primary murine adipocytes from differentiated white fat precursor cells (Hiroyama, et al., 2009).
- Lipolysis Kit used to measure lipolysis after treatment of primary adipocytes with isoproterenol or recombinant leptin (Cernkovich, Deng, Bond, Combs, & Harp, 2008).
- Glycerol reagent (lipolysis kit) used to measure lipolysis change in cells after Guggulsterone treatment (Yang, Della-Fera, & Baile, 2008).
- Glycerol reagent (lipolysis kit) used to measure change in triglyceride hydrolysis following injection of antimicrobial peptide dermicidin in vivo (K.-A. Kim, et al., 2008).
- Lipolysis assay kit used to measure FFA released from mature adipocytes and media from breast cancer cells (J. H. Kim, et al., 2008).
- Lipolysis assay kit used in adipose-derived stem cells aging study (Schipper, Marra, Zhang, Donnenberg, & Rubin, 2008).
LIP-2
- FFA kit used in patients for angiopoietin study (Robciuc, Tahvanainen, Jauhiainen, & Ehnholm, 2010).
- FFA kit used in liver steatosis study in SIRT1 knockout mice (Xu, et al., 2010).
- FFA kit used in an oxidative stress study to determine the interaction between dyslipidemia and inflammation in obese children (Oliver, et al., 2010).
- FFA kit used to support circadian rhythm analysis in rat adipose tissue (Sukumaran, Xue, Jusko, Dubois, & Almon, 2010).
- FFA kit used to measure FFA after diet restriction in two rock climbers, oxidative stress study (Merrells, Friel, Knaus, & Suh, 2008).
LIP-3
- TG/FFA kit used to measure regulation of serum lipids by Pck1 in insulin resistant mice (Millward, et al., 2010).
- TG/FFA kit used to measure lipolysis and triglyceride accumulation in adipocytes after treatment with all-trans retinoic acid (Berry, Soltanian, & Noy, 2010).
- TG/FFA kit used to measure triglycerides and lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells after treatment with dexamethasone and methylisobutylxanthine (Pantoja, Huff, & Yamamoto, 2008).
LIP-1-LI
- Adipocyte lipolysis assay kit use to measure white adipocyte lipolysis activation (An, et al., 2010).
- 3T3-L1 adipocytes triglyceride lipolysis kit used to measure PPAR-Gamma effects on lipid storage (Lobo, et al., 2010).
- 3T3-L1 Adipocyte kit used to prepare cells for mineralcorticoid receptor blockade experiments (Guo, et al., 2008).
Lipolysis Kits Publications
Dopamine D2 receptor agonist, bromocriptine, remodels adipose tissue dopaminergic signalling and upregulates catabolic pathways, improving metabolic profile in
G. Tavares, D. Marques, C. Barra, D. Rosendo-Silva, A. Costa, T. Rodrigues, P. Gasparini, B.F. Melo, J.F. Sacramento, R. Seiça, S.V. Conde, P. Matafome https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101241ADORA 1-driven brain-sympathetic neuro-adipose connections control body weight and adipose lipid metabolism
Jia Zhang, Yanjun Hou, Xue-liang Du, Dan Chen, Guangzhi Sui, Yong Qi, Julio Licinio, Ma-Li Wong & Yunlei YangDOIhttps://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-00908-y
Effects of PCB126 on Adipose-to-Muscle Communication in an in Vitro Model
Audrey Caron, Fozia Ahmed, Vian Peshdary, Léa Garneau, Ella Atlas, and Céline Aguerhttps://doi.org/10.1289/EHP7058.
Mitoregulin Controls b-Oxidation in Human and Mouse Adipocytes
Max Friesen, Curtis R. Warren, Haojie Yu, Takafumi Toyohara, Qiurong Ding, Mary H.C. Florido, Carolyn Sayre, Benjamin D. Pope, Loyal A. Goff, John L. Rinn, and Chad A. Cowanhttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.03.002
Mitoregulin Controls β-Oxidation in Human and Mouse Adipocytes
Max Friesen, Curtis R. Warren, Haojie Yu, Takafumi Toyohara, Qiurong Ding, Mary H.C. Florido, Carolyn Sayre, Benjamin D. Pope, Loyal A. Goff, John L. Rinn, Chad A. Cowanhttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.03.002
Cell-autonomous light sensitivity via Opsin3 regulates fuel utilization in brown adipocytes
Mari Sato, Tadataka Tsuji, Kunyan Yang, Xiaozhi Ren, Jonathan M. Dreyfuss, Tian Lian Huang, Chih-Hao Wang, Farnaz Shamsi, Luiz O. Leiria, Matthew D. Lynes, King-Wai Yau, Yu-Hua TsengDOI https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000630
Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester and Its Fluorinated Derivative as Natural Anti-obesity Agents (P06-089-19)
Srujana Rayalam, Devin Mills, Yusra Azhar, Ebony Miller, and Xinyu WangPhiladelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine - GA Campus
Adipose HuR protects against diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance
Jingyuan Li, Li Gong, Shaozhuang Liu, Yujie Zhang, Chunmei Zhang, Mi Tian, Huixia Lu, Peili Bu, Jianmin Yang, Changhan Ouyang, Xiuxin Jiang, Jiliang Wu, Yun Zhang, Qing Min, Cheng Zhang & Wencheng ZhangDOI https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10348-0
Role of Adipose-to-Muscle Communication in PCB126-induced Metabolic Defects
Audrey CaronA Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the MSc Degree in Biochemistry
Bovine Tissue-Scaffold Interface Facilitates in vivo Evaluation of Tissue-Engineered Injectable Devices for Breast Tissue Reconstruction
Y Khan, CT Laurencin - Regenerative Engineering, 2018Histone demethylase JMJD1A coordinates acute and chronic adaptation to cold stress via thermogenic phospho-switch
Yohei Abe, Yosuke Fujiwara, Hiroki Takahashi, Yoshihiro Matsumura, Tomonobu Sawada, Shuying Jiang, Ryo Nakaki, Aoi Uchida, Noriko Nagao, Makoto Naito, Shingo Kajimura, Hiroshi Kimura, Timothy F. Osborne, Hiroyuki Aburatani, Tatsuhiko Kodama, Takeshi Inagaki & Juro Sakaidoi:10.1038/s41467-018-03868-8
DEHP deregulates adipokine levels and impairs fatty acid storage in human SGBS-adipocytes
Kristina Schaedlich, Scarlett Gebauer, Luise Hunger, Laura-Sophie Beier, Holger M. Koch, Martin Wabitsch, Bernd Fischer & Jana Ernstdoi:10.1038/s41598-018-21800-4
Regulation of Lipolytic Response and Energy Balance by Melanocortin 2 Receptor Accessory Protein (MRAP) in Adipocytes Xiaodong Zhang, Alicia M. Saarinen, Latoya E. Campbell, Elena A. De Filippis and Jun Liu
Diabetes 2017 Dec; db170862.https://doi.org/10.2337/db17-0862
Fucoxanthin and its Metabolite Fucoxanthinol Do Not Induce Browning in Human Adipocytes
Candida J. Rebello, Frank L. Greenway, William Johnson, David Ribnicky, Alexander Poulev, Krisztian Stadler, and Ann CoulterJ. Agric. Food Chem., DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03931
Human ADMC-Derived Adipocyte Thermogenic Capacity Is Regulated by IL-4 Receptor
Fernando Lizcano, Diana Vargas, Ãngela Gómez, and Astrid Torradohttps://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2767916
Role of sulfotransferases in resveratrol metabolism in human adipocytes
Nele Gheldof, Sofia Moco, Christian Chabert, Tony Teav, Denis Barron, Jorg HagerDOI: 10.1002/mnfr.201700020
Specific macronutrients exert unique influences on the adipose-liver axis to promote hepatic steatosis in mice
Duwaerts CC, Amin AM, Siao K, Her C, Fitch M, Beysen C, Turner SM, Goodsell A, Baron JL, Grenert JP, Cho S-J, Maher JJCellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology (2017), doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.04.004
The role of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity in mediating the relationship between central adiposity and immunometabolic profile in postmenopausal women
Tiego A. Diniz, Fabricio E. Rossi, Loreana S. Silveira, Lucas Melo Neves, Ana Claudia de Souza Fortaleza, Diego G. D. Christofaro, Fabio S. Lira, Ismael F. Freitas Juniorhttp://dx.doi.org/10.1590/2359-3997000000259
Mfn2 is critical for brown adipose tissue thermogenic function
Marie Boutant, Sameer S Kulkarni, Magali Joffraud, Joanna Ratajczak, Miriam Valera-Alberni, Roy Combe, Antonio Zorzano and Carles Cant´o;DOI 10.15252/embj.201694914 | Published online 27.03.2017
Adipocyte arrestin domain-containing 3 protein (Arrdc3) regulates uncoupling protein 1 (Ucp1) expression in white adipose independently of canonical changes in β- ...
Shannon H. Carroll, Ellen Zhang, Bing F. Wang, Katherine B. LeClair, Arifeen Rahman, David E. Cohen, Jorge Plutzky, Parth Patwari, Richard T. Leehttp://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173823
Biological activities of the legume crops Melilotus officinalis and Lespedeza capitata for skin care and pharmaceutical applications
Giulia Pastorinoa, Carla Marchettib, Barbara Borghesia, Laura Cornaraa, Stefania Ribullac, Bruno Burlandobhttp://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.11.047
Whole-exome sequencing identifies ADRA2A mutation in atypical familial partial lipodystrophy
Abhimanyu Garg,1 Shireesha Sankella,1 Chao Xing,2 and Anil K. AgarwalJCI Insight. 2016;1(9):e86870. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.86870
The ubiquitin ligase Siah2 regulates obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation
Gail Kilroy, Lauren E. Carter, Susan Newman, David H. Burk, Justin Manuel, Andreas Möller, David D. Bowtell, Randall L. Mynatt, Sujoy Ghosh, and Z. Elizabeth FloydArticle first published online: 18 SEP 2015, OBESITY DOI: 10.1002/oby.21220
Tissue Inhibitor Of Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 Is Required for High-Fat Diet-Induced Glucose Intolerance and Hepatic Steatosis in Mice
Even Fjære, Charlotte Andersen, Lene Secher Myrmel, Rasmus Koefoed Petersen, Jakob Bondo Hansen, Hanne Sørup Tastesen, Thomas Mandrup-Poulsen, Nils Brünner, Karsten Kristiansen, Lise Madsen, Maria Unni RømerDOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132910
Age-related lipid metabolic signature in human LMNA-lipodystrophic stem cell derived adipocytes
Patricia Sánchez, Arantza Infante, Garbiñe Ruiz de Eguino, Jorge A. Fuentes-Maestre, José Manuel García-Verdugo, and Clara I. Rodríguezdoi: 10.1210/jc.2014-4528, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Group IIE secretory phospholipase A2 regulates lipolysis in adipocytes
H Zhi, L Qu, F Wu, L Chen, J TaoObesity, 2015 9 MAR 2015 DOI: 10.1002/oby.21015
Hypermetabolism of Fat in V1a Vasopressin Receptor Knockout Mice.
Masami Hiroyama, Toshinori Aoyagi, Yoko Fujiwara, Junichi Birumachi, Yosuke Shigematsu, Kohji Kiwaki, Ryuji Tasaki, Fumio Endo, and Akito TanoueMol. Endocrinol., Jan 2007; 21: 247 - 258.
Thrombin increases inflammatory cytokine and angiogenic growth factor secretion in human adipose cells in vitro.
J. L. Strande and S. A. PhillipsJ Inflamm (Lond). 2009; 6 4.
Monoclonal antibody antagonists of hypothalamic FGFR1 cause potent but reversible hypophagia and weight loss in rodents and monkeys.
Haijun D. Sun, Maria Malabunga, James R. Tonra, Roberto DiRenzo, Francine E. Carrick, Huiyuan Zheng, Hans-Rudolf Berthoud, Owen P. McGuinness, Juqun Shen, Peter Bohlen, Rudolph L. Leibel, and Paul KussieAm J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, Mar 2007; 292: E964 - E976.
Adipocyte culture medium stimulates production of macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1 in MDA-MB-231 cells.
Kim, Jae Hyeong, Kim, Kun-yong, Jeon, Jun Ho, Lee, Su Hee, Hwang, Ji-Eun, Lee, Jung Hyeonget al. 2008. Cancer letters; 261: 253-262.
Adipose-specific disruption of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 increases body weight and adiposity.
Cernkovich, Erin R, Deng, Jianbei, Bond, Michael C, Combs, Terry P, & Harp, Joyce B2008. Endocrinology; 149: 1581-1590.
Altered lipid metabolism in vasopressin V1B receptor-deficient mice.
Hiroyama, M., Fujiwara, Y., Nakamura, K., Aoyagi, T., Mizutani, R., Sanbe, A.et al. 2009. Eur J Pharmacol; 602: 455-461.
Anti-obesity effects of xanthohumol plus guggulsterone in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
Rayalam, Srujana, Yang, Jeong-Yeh, Della-Fera, Mary Anne, Park, Hea Jin, Ambati, Suresh, & Baile, Clifton A2009. Journal of medicinal food; 12: 846-853.
Differential regulation of adipocyte PDE3B in distinct membrane compartments by insulin and the beta3-adrenergic receptor agonist CL316243: effects of caveolin-1 knockdown on formation/maintenance of macromolecular signalling complexes.
Ahmad, F., Lindh, R., Tang, Y., Ruishalme, I., Ost, A., Sahachartsiri, B.et al. 2009. Biochem J; 424: 399-410.
Effect of dermcidin, an antimicrobial peptide, on body fat mobilization in normal mice.
Kim, Kyung-Ah, Ka, Sun-O, Moon, Woo Sung, Yi, Ho-Keun, Lee, Young-Hoon, Kwon, Kang-Beomet al. 2008. The Journal of endocrinology; 198: 111-118.
GPR103b functions in the peripheral regulation of adipogenesis.
Mulumba, M., Jossart, C., Granata, R., Gallo, D., Escher, E., Ghigo, E.et al. Mol Endocrinol; 24: 1615-1625.
Guggulsterone inhibits adipocyte differentiation and induces apoptosis in 3T3-L1 cells.
Yang, Jeong-Yeh, Della-Fera, Mary Anne, & Baile, Clifton A2008. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.); 16: 16-22.
In vitro studies investigating the effect of subcutaneous phosphatidylcholine injections in the 3T3-L1 adipocyte model: lipolysis or lipid dissolution?
Klein, S. M., Schreml, S., Nerlich, M., & Prantl, L.2009. Plast Reconstr Surg; 124: 419-427.
Lactate inhibits lipolysis in fat cells through activation of an orphan G-protein-coupled receptor, GPR81.
Liu, C., Wu, J., Zhu, J., Kuei, C., Yu, J., Shelton, J.,et al. 2009. J Biol Chem; 284: 2811-2822.
Regional anatomic and age effects on cell function of human adipose-derived stem cells.
Schipper, B. M., Marra, K. G., Zhang, W., Donnenberg, A. D., & Rubin, J. P.2008. Ann Plast Surg; 60: 538-544.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone stimulates lipolysis in adipocytes in culture and raises serum free fatty acid levels in vivo.
Gagnon, Annemarie, Antunes, Tayze T, Ly, Tapraya, Pongsuwan, Patama, Gavin, Claire, Lochnan, Heather A,et al. 2010. Metabolism: clinical and experimental; 59: 547-553.
Beta-carotene decreases peroxisome proliferator receptor gamma activity and reduces lipid storage capacity of adipocytes in a beta-carotene oxygenase 1-dependent manner.
Lobo, G.P.; Amengual, J.; Li, H.N.; Golczak, M.; Bonet, M.L.; Palczewski, K.; von Lintig, J. J. Biol. Chem.2010, 285, 27891-27899.
Ethanolic extracts of Brassica campestris spp. rapa roots prevent high-fat diet-induced obesity via beta(3)-adrenergic regulation of white adipocyte lipolytic activity.
An, Sojin, Han, Jang-Il, Kim, Min-Jung, Park, Ji-Seon, Han, Jong-Min, Baek, Nam-Inet al. 2010. Journal of medicinal food; 13: 406-414.
Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade reverses obesity-related changes in expression of adiponectin, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, and proinflammatory adipokines.
Guo, Christine, Ricchiuti, Vincent, Lian, Bill Q, Yao, Tham M, Coutinho, Patricia, Romero, José Ret al. 2008. Circulation; 117: 2253-2261.
CIRCADIAN VARIATIONS IN GENE EXPRESSION IN RAT ABDOMINAL ADIPOSE TISSUE AND RELATIONSHIP TO PHYSIOLOGY.
Sukumaran, Siddharth, Xue, Bai, Jusko, William J, Dubois, Debra C, & Almon, Richard R2010. Physiological genomics; 42A: 141-152.
Following 2 diet-restricted male outdoor rock climbers: impact on oxidative stress and improvements in markers of cardiovascular risk.
Merrells, K. J., Friel, J. K., Knaus, M., & Suh, M.2008. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab; 33: 1250-1256.
Increased oxidative stress and altered substrate metabolism in obese children.
Oliver, Stacy R, Rosa, Jaime S, Milne, Ginger L, Pontello, Andria M, Borntrager, Holly L, Heydari, Shirinet al. 2010. International journal of pediatric obesity : IJPO : an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity; 5: 436-444.
Lack of SIRT1 (Mammalian Sirtuin 1) activity leads to liver steatosis in the SIRT1+/- mice: a role of lipid mobilization and inflammation.
Xu, Fen, Gao, Zhanguo, Zhang, Jin, Rivera, Chantal A, Yin, Jun, Weng, Jianpinget al. 2010. Endocrinology; 151: 2504-2514.
Quantitation of serum angiopoietin-like proteins 3 and 4 in a Finnish population sample.
Robciuc, Marius R, Tahvanainen, Esa, Jauhiainen, Matti, & Ehnholm, Christian2010. Journal of lipid research; 51: 824-831.
Glucocorticoid signaling defines a novel commitment state during adipogenesis in vitro.
Pantoja, Carlos, Huff, Jason T, & Yamamoto, Keith R2008. Molecular biology of the cell; 19: 4032-4041.
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pck1) helps regulate the triglyceride/fatty acid cycle and development of insulin resistance in mice.
Millward, Carrie A, Desantis, David, Hsieh, Chang-Wen, Heaney, Jason D, Pisano, Sorana, Olswang, Yaelet al. 2010. Journal of lipid research; 51: 1452-1463.
Repression of cellular retinoic acid-binding protein II during adipocyte differentiation.
Berry, Daniel C, Soltanian, Hooman, & Noy, Noa2010. The Journal of biological chemistry; 285: 15324-15332.