ZenComplete™: Rodent Lipolysis
Lipolysis plays a central role in the regulation of energy balance. Lipolysis is the process in which triglycerides (TG) are hydrolyzed into glycerol and free fatty acids. This process releases free fatty acids (FFA) into the bloodstream where they may be either re-esterified by the adipocyte or travel to other tissues and exert other effects throughout the body. Elevated adipocyte lipolysis has been observed in obese and diabetic individuals (Arner 1996). Excessive free fatty acid production is believed to contribute to insulin resistance in skeletal muscle that is observed in obesity. Hormone sensitive lipase is the rate-limiting enzyme catalyzing triglyceride breakdown. Perilipins, one of the PAT (perilipins, adipophilin, TIP47 proteins) family of lipid-associated proteins, are implicated in adipocyte lipolysis by mediating the interaction of HSL with the triacylglycerol molecule (Brasaemle et al. 2004; reviewed in, Tansey et al. 2004.) The presence of these proteins corresponds to lipolytic stimulation in cultured adipocytes (Braemle et al. 2004).
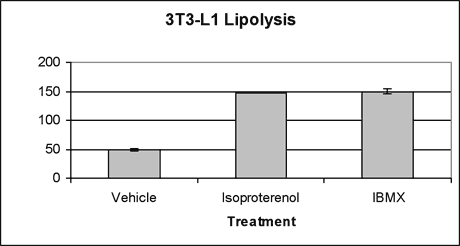
- Positive controls: isoproterenol (1 µM), IBMX (100µM)
- Vehicle Control: Appropriate concentration of all solvents
- Treatment: 3-5 hours
Treatments will be done in triplicate at concentrations indicated by contact scientists. All treatments will be for. At the end of treatment period conditioned media will be removed and glycerol concentration determined by GPO-Trinder reagent. We can offer custom assay comparison services in parallel with out human adipocyte cell system. Please inquire of our contract assay team for more information.
Ordering Information
| Item# | Item Desc | U/M | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA-310 | 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Lipolysis Assay (glycerol release) | Assay | Call |
| CA-311 | 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Lipolysis Assay (free fatty acid release) | Assay | Call |
| CA-312 | 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Lipolysis Assay (glycerol and FFA release) | Assay | Call |
REFERENCES:
Arner P (1996) Diabetes Rev 4(4):450-463.
Brasaemle DL, Dolios G, Shapiro L, Wang R. (2004) J Biol Chem 279(45): 46835-42.
Cooper DMF, Schlegel W, Lin MC, Rodbell M. (1979) J Biol Chem 254(18):8927-8931.
Tansey JT, Sztalryd C, Hlavin EM, Kimmel AR, Londos C. (2004) IUBMB Life 56(7): 379-85.
To learn more about our services, please contact our Services Team



